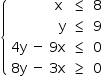Uma região de uma fábrica deve ser isolada, pois nela os
empregados ficam expostos a riscos de acidentes. Essa
região está representada pela porção de cor cinza
(quadrilátero de área S) na figura.
Para que os funcionários sejam orientados sobre a
localização da área isolada, cartazes informativos serão
afixados por toda a fábrica. Para confeccioná-los, um
programador utilizará um software que permite desenhar
essa região a partir de um conjunto de desigualdades
algébricas.
As desigualdades que devem ser utilizadas no referido
software, para o desenho da região de isolamento, são
a) 3y – x ≤ 0; 2y – x ≥ 0; y ≤ 8; x ≤ 9
b) 3y – x ≤ 0; 2y – x ≥ 0; y ≤ 9; x ≤ 8
c) 3y – x ≥ 0; 2y – x ≤ 0; y ≤ 9; x ≤ 8
d) 4y – 9x ≤ 0; 8y – 3x ≥ 0; y ≤ 8; x ≤ 9
e) 4y – 9x ≤ 0; 8y – 3x ≥ 0; y ≤ 9; x ≤ 8
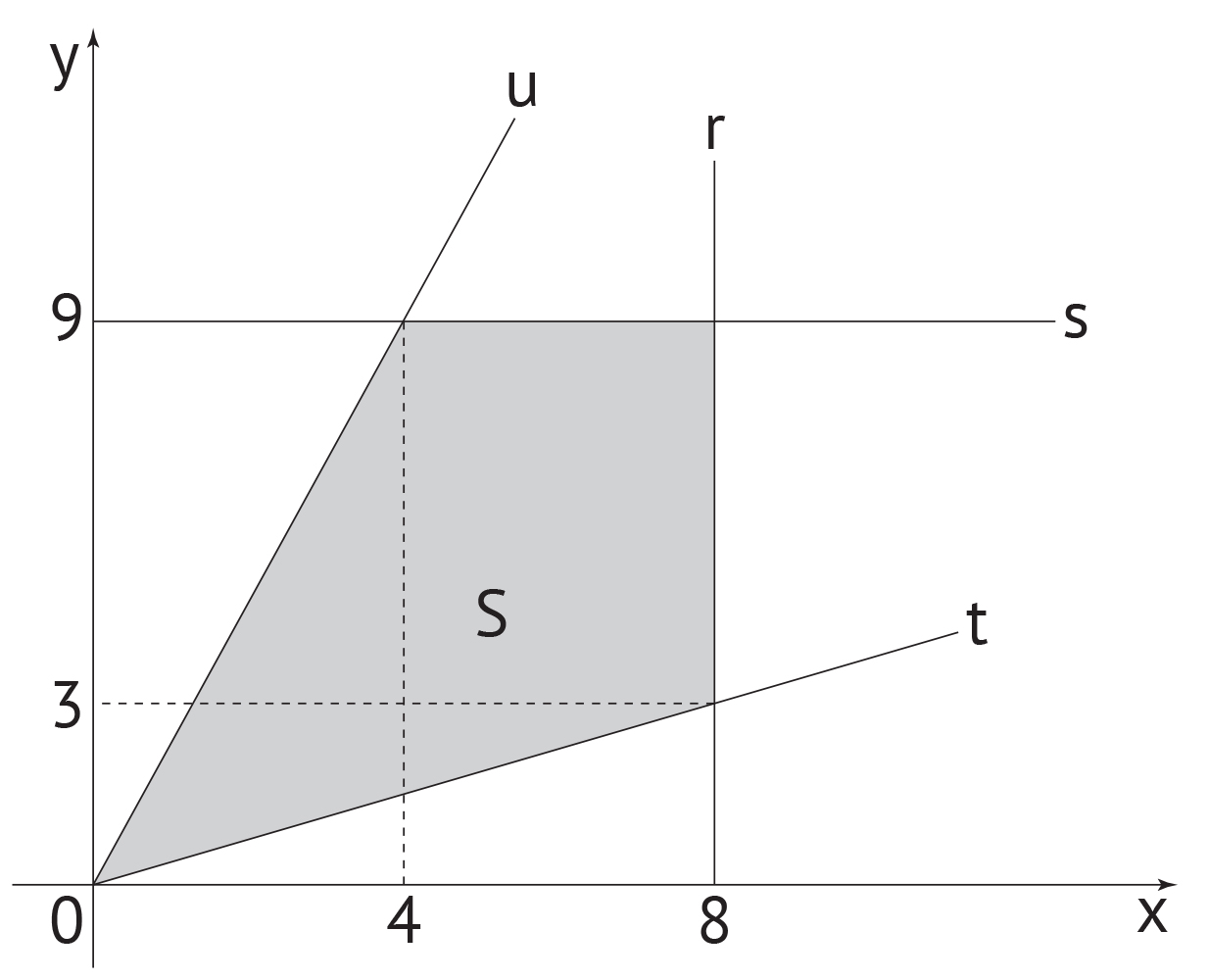
A partir da figura, temos as equações das retas:
- reta r:
A reta r é uma reta vertical; portanto, sua equação é dada por x = 8;
- reta s:
A reta s é uma reta horizontal; portanto, sua equação é dada por y = 9;
- reta t:
A reta t passa pelos pontos (0, 0) e (8, 3). Assim, seu coeficiente angular é dado por 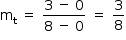 e, portanto, uma equação é dada por
e, portanto, uma equação é dada por 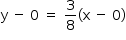 , ou seja,
, ou seja, 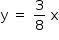 .
.
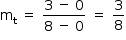 e, portanto, uma equação é dada por
e, portanto, uma equação é dada por 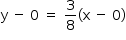 , ou seja,
, ou seja, 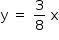 .
.- reta u:
A reta u passa pelos pontos (0, 0) e (4 , 9). Assim, seu coeficiente angular é dado por 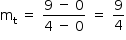 e, portanto, uma equação é dada por
e, portanto, uma equação é dada por 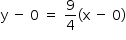 , ou seja,
, ou seja, 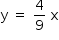 .
.
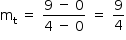 e, portanto, uma equação é dada por
e, portanto, uma equação é dada por 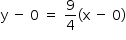 , ou seja,
, ou seja, 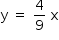 .
.
A região S pode ser descrita através do seguinte sistema de inequações:
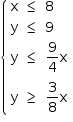
que é equivalente ao sistema: